13.1. OASIS philosophy¶
13.1.1. OASIS libraries¶
OASIS-MCT libraries are:
psmile for coupling
mct (Argonne National Laboratory) for parallel exchanges
scrip (Los Alamos National Laboratory) for interpolations
Functions provided by the OASIS-MCT framework are:
Note
oasis_/prism_are new / old names for backward compatibility, both useable
Initialization and creation of a local communicator for internal parallel computation in each model:
oasis_init_comp / prism_init_comp_proto
oasis_get_localcomm / prism_get_localcomm_proto
Grid data definition for exchanges and interpolations:
oasis_write_grid
oasis_write_corner
oasis_write_area
oasis_write_mask
oasis_terminate_grids_writing
Partition and exchanged variables definition:
oasis_def_partition / prism_def_partition_proto
oasis_def_var / prism_def_var_proto
oasis_enddef / prism_enddef_proto
Exchange of coupling fields:
oasis_get / prism_get_proto
oasis_put / prism_put_proto
Finalization:
oasis_terminate / prism_terminate_proto
These OASIS3-MCT intrinsic functions are called in each model involved in the coupling. Initialization phase, Definition phase, and Finalization phase are called only once in each simulation while Exchange phase is called every time step. The effective exchanges are done only at specified times, defined by the coupling frequency, although the Exchange phase is called every model time step. The coupling frequency is controlled through the OASIS3-MCT namcouple.
13.1.2. Coupling sequence¶
The frequency of exchanges between two models is defined by the coupling time step.
The coupling time step must be a multiple of the models time steps. An example of coupling sequence is pictured in the following Figure. In this example, the coupling time step is defined at 360s for both models. The wave model time step is 90s, so it will exchange every 4 time steps. The ocean model time step is 180s, so it will exchange every 2 time steps.
Another coupling parameter defined in the namcouple is the lag. It is used by the OASIS coupler to synchronize the send and receive functions. The lag must be defined for each model at the same value than its own time step. For instance:
WAVE to OCEAN
lag = dt wave = 90OCEAN to WAVE
lag = dt ocean = 180
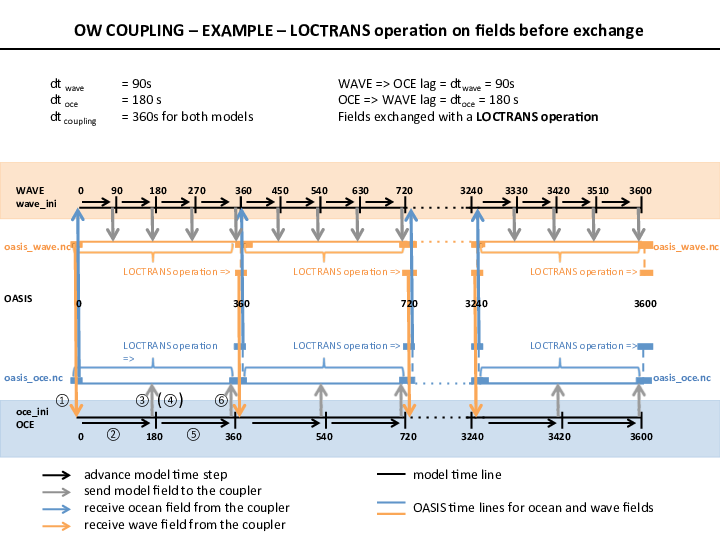
Therefore, receive and send functions have to be set at the same time in the model codes. OASIS will send the fields at the appropriate time thanks to the lag defined in the namcouple.
The coupling sequence in each model is:
initialization |
|
reception of coupled fields |
|
model time stepping |
computation |
sending of coupled fields |
|
increment of coupling time |
|
OASIS will exchange fields (get/put) if the time corresponds to a coupling time step, e.g. if:
oasis_timecorresponds to a coupling time step for get
oasis_time + lagcorresponds to a coupling time step for put
IN THE MODEL |
IN OASIS |
|---|---|
receive (date) |
get(date) |
send(date) |
put(date+lag) |
OASIS is also able to store fields from a model if a time transformation is requested in the namcouple (keyword LOCTRANS + type of transformation, see next section). OASIS will store the fields until a coupling time step is reached, then it will apply the time transformation, interpolate spatially the field as specified in the namcouple, and exchange the field with the other model.
13.1.3. Restart files¶
As reception of coupled fields is called before model computation, you need to create restart files for the coupler containing initial or restart fields for the first time step.
These restart files are for OASIS, and therefore need to have variable names corresponding to OASIS namcouple coupled fields. The initial files for OASIS are named oasis_oce.nc and oasis_wave.nc in the example pirctured in the above Figure. oce_ini and wave_ini are not related to OASIS, they are usual initialization or restart files from your oceanic and wave model; e.g. in CROCO, oce_ini is croco_ini.nc, and in WW3, wave_ini is restart.ww3).
- Summary of the restart files:
oasis_oce.nc,oasis_wave.nc: restart files for OASIS, you need to create them at the beginning of the run, OASIS will overwrite them at the end of the run, and they will be available for next restartoce_ini,wave_ini: correspond tocroco_ini.nc,restart.ww3. These are your ocean and wave model initial or restart files
Practical example of the coupling sequence pictured in the above Figure:
oasis_time = 0
#1 => get field from oasis_wave.nc
rcv(0) => in oasis: get(0)
#2 => timestepping
t = 0+dt = 0+180 = 180
#3 => 180 is not a coupling time step, do nothing
snd(0) => in oasis: put(0+lag) = put(0+180) = put(180)
oasis_time = oasis_time+dt = 0+180 = 180
#4 => 180 is not a coupling time step, do nothing
rcv(180) => in oasis: get(180)
#5 => timestepping
t = 180+dt = 180+180 = 360
#6 => 360 is a coupling time step, put field
snd(180) => in oasis: put(180+lag) = put(180+180) = put(360)
13.1.4. Interpolations¶
The OASIS3-MCT coupler can process time transformations and 2D spatial interpolations of the exchanged fields.
The 2D spatial interpolation, requested if models have different grids, is performed by the scrip library using SCRIPR keyword in the namcouple. Available interpolation types are:
|
interpolation based on a local bilinear approximation |
|
interpolation based on a local bicubic approximation |
|
1st or 2nd order conservative remapping |
|
distance weighted nearest-neighbour interpolation (N neighbours) |
|
N nearest-neighbour interpolation weighted by their distance
and a gaussian function
|
See OASIS manual for detailed informations.
Time transformations can also be performed by OASIS using LOCTRANS keywork in the namcouple. Available transformations are:
|
no time transformation, the instantaneous field is transfered |
|
the field accumulated over the previous coupling period is exchanged |
|
the field averaged over the previous coupling period is transfered |
|
the minimum value of the field for each source grid point over the
previous coupling period is transfered
|
|
the maximum value of the field for each source grid point over the
previous coupling period is transfered
|